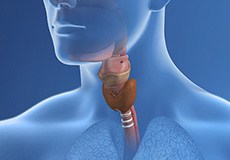
Procedures
Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
Endoscopic sinus surgery is a procedure that involves the use of an endoscope, a fiberoptic tube-like instrument, to open the natural drainage pathways of the sinuses and restore their health and function.
Direct Laryngoscopy
A direct laryngoscopy is a procedure that involves the use of a laryngoscope, a special tube-like instrument which allows your doctor to directly visualize your larynx, also known as the voice box, which is in the back of your throat. The larynx contains your vocal cords and helps with talking, swallowing, and breathing.
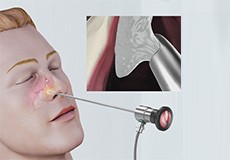
Nasal Polypectomy
Nasal polypectomy is a surgery performed to remove nasal polyps, which are non-cancerous, fleshy growths that develop in the mucosal lining of the nasal and paranasal sinuses. Small nasal polyps usually do not cause any symptoms, but larger polyps or groups of polyps can obstruct the nasal passages and cause problems with breathing.

Septoplasty
Septoplasty is a surgery performed to straighten or reposition the nasal septum to the midline of the nose. The nasal septum is a cartilaginous and bony structure that separates the right and left nostrils.
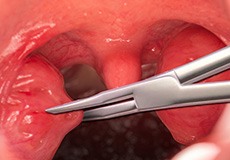
Adult Tonsillectomy
Adult tonsillectomy is surgical procedure performed to remove both tonsils which are the two lumps of tissue located at the back of the oral cavity on either side of the throat of an adult patient.

Tonsillectomy/Adenoidectomy (Pediatric)
Pediatric tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy are surgical procedures performed to remove both tonsils which are the two lumps of tissue located at the back of the oral cavity on either side of the throat, and adenoids which is a mass of tissue at the back of the nasal cavity in children.
Mastoidectomy
Mastoidectomy is a surgery performed to remove diseased mastoid air cells from the mastoid bone located in the skull behind the ear. The mastoid bone is filled with air cells made of bone and looks similar to a honeycomb. The term “cells” refers to the enclosed spaces of the bone.
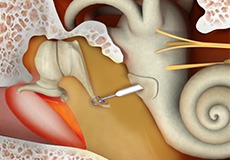
Stapedotomy
A stapedotomy is a surgery performed in the ear to improve hearing. It involves the creation of a precise hole in the footplate of the stapes, which is a bone in the middle ear; and the placement of a micro-prosthesis. The footplate of the stapes covers the opening to the inner ear and helps carry vibration of sound into the inner ear.
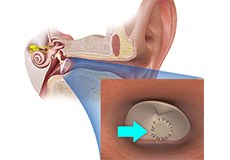
Tympanoplasty
Tympanoplasty is a surgery performed to repair a perforation in the tympanic membrane, also known as the eardrum. The tympanic membrane is a thin, translucent membrane that covers the end of the external auditory canal and separates the outer ear from the middle ear.

Cochlear Implants
Cochlear implantation is a procedure for the treatment of severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) in both children and adults. A cochlear implant is a device inserted into your ear to help in hearing.
Conditions
Head and Neck Cancer
At Central Coast Head and Neck Surgeons, we have a team of highly trained and experienced surgeons in oncologic surgery, to provide you with the best treatment available. We work closely with our colleagues in radiation oncology, medical oncology, speech and swallow therapists, and occupational and physical therapists to provide a multidisciplinary approach to treatment, which is personalized and tailored to the patient.
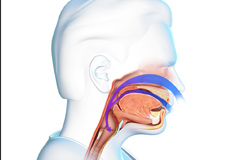
Voice Disorders
Voice is the sound produced by humans and other vertebrates using the lungs and the vocal folds in the larynx, or voice box. Voice is not always produced as speech, however. Infants babble and coo; animals bark, moo, whinny, growl, and meow; and adult humans laugh, sing, and cry.
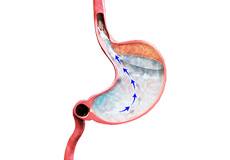
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Your stomach is filled with acid. Its purpose is to help digest the food you eat. Believe it or not, this acid is as strong as battery acid. Your stomach is built to handle it. Your esophagus and throat are not. When acid backs up into your esophagus, it can cause the burning sensation known as heartburn.
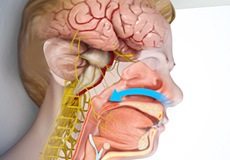
Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea describes a sleep disorder characterized by frequent pauses in breathing due to collapse or obstruction of the airway. It is quite a common disorder and affects around 4% of the population.
Anatomy
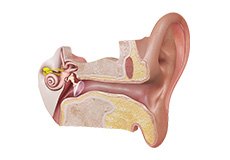
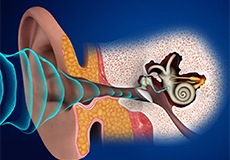
Anatomy of the Ear
The human ear is an organ concerned with hearing and equilibrium. It converts sound waves into electrochemical signals that are interpreted by the brain and helps you maintain your sense of balance. Anatomically, the ear can be divided into the outer ear, the tympanic membrane, the middle ear, and the inner ear.
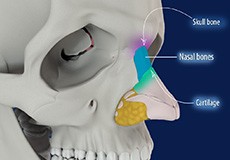
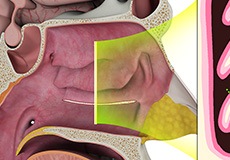
Anatomy of the Nose
The nasal passages serve as an entrance to the respiratory tract. These passages are lined by a moist mucous membrane with hair-like projections known as cilia which help collect dust, debris, and bacteria.