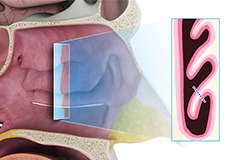
The nasal turbinates are bony structures covered with mucosa and vascular tissue which are located on the inside of the nose on each side. When these are large or swollen, from colds or allergies, they can obstruct airflow and make breathing difficult through the nose.
Turbinoplasty involves using heat to shrink this tissue, so that air can more easily pass. A special type of device is ofen used called a coblator, a long slender needle which heats the tissues to a specific temperature to allow shrinkage but not damage to surrounding tissue. In the office setting, this can be done after the nasal cavities are anesthetized with local anesthesia, so that the patient does not feel any pain during the procedure. The procedure lasts around 15 minutes, and following this the patient can resume normal activities. Often postop visits are needed to remove crusting as the turbinates heal.
